When you’re looking to build a PC, one of the most important considerations is the wattage of your power supply. Not all power supplies are created equal, and the wattage you need will vary depending on the components you use. Such factors force you to consider; how to choose the power supply wattage for your computer. To help you, in this article, we’ll show you how to measure your power supply wattage for different PC builds and help you choose the right power supply for your needs.
How To Choose Power Supply Wattage?
When choosing a power supply, it is important to select one with the correct wattage for your system. This is the maximum amount of power that the supply can output. If you select a supply with too low of wattage, it may not be able to handle the load and could result in damage to your system or components.
Following these steps you can easily choose your power supply’s wattage:
Step One: Know And Choose From Three Main Types Of PSU
The first step is to identify the PSU type from 3 main types. This information should be printed on the label on the back of the unit. Once you have this information, you can then choose either option for ease of use. Which is selecting the modular, semi-modular, or non-modular type.
Step Two: Determine How Many Watts Your System Requires
Next, you will need to determine how many watts your system requires. You can do this by checking your computer’s documentation or by using a software utility such as CPU-Z or checking your CPU’s official box for the maximum wattage requirements and the OC, which should be extended than the original limits.
Step Three: Choose PSU According To Your PC Hardware
We all know that PC hardware is exploding with new technology every year, which increases the power usage by individual components that are more powerful and more capable than previous-generation. This varies greatly depending on your system configuration.
Step Four: Know Your Lowest And Maximum Power Supply Requirement
If you want to install a dedicated GPU, the power requirements will be higher than if you only used a CPU with an iGPU (Integrated Graphics). To determine an ideal power supply wattage, consider how powerful your graphics card is and what its maximum power usage is.
Step Five: Identify Your System Power Hungry Components
More complex systems, such as desktop gaming PC with dual GPUs, and a high-end CPU with a custom liquid cooling loop (waterblock), all require more power to run than a simpler system with a single GPU and moderate CPU with limited additional SSDs and HDDs.
With the help of these ground-up steps, you’ve determined how much wattage you’ll require for your newly built PC which is based on four main components; your CPU, GPU, Waterblock, and storage devices. Down below I’ve described simple methods for properly calculating all of your PC components’ power requirements to purchase a capable PSU.
Three Methods To Choose Power Supply Wattage Requirement For Your PC
Method One: Look At Specifications And Manuals
The first is to look at the specifications of your computer and individual components. Your computer’s manual lists the system requirements, including the minimum required wattage. You can also find this information online or on the packaging for your components.
Method Two: Using A PSU Calculator
The second way to estimate your wattage needs is by using a PSU calculator. This takes into account all of the components in your system and their respective power requirements. There are several online calculators available, or you can use one from a trusted manufacturer like Corsair or Antec.
Method Three: Manual Way To Calculate Your Power Supply Wattage
It’s impossible to make a specific recommendation without knowing precisely what hardware you’re working with, but determining the power draw of your various internal components and adding that together, can help.
What you need for manual calculation is knowing your components and determining which hardware components are compatible with which PSU? Which I did this way.
First, let’s take a look at what important factors can affect your power supply needs, means most power-hungry components to consider are:
Recorded Most Power Hungry PC Components
1) The type of CPU: How powerful is your CPU, requires a higher wattage PSU.
2) The number of Graphics Cards (4K): The more powerful the GPU, the more power the system will require. If you have more than one, you will need a 1K+ PSU.
3) Liquid cooling system: Your PC cooling solution will weigh on your PSU capacity.
Editor Tips:
- If you have a high-end Intel CPU that requires more power than a low-power AMD CPU, then you’ll need a higher wattage power supply.
- If you have a lot of graphics cards, then you may need more power. If you have a lot of storage drives, then you may need more power.
- There are other factors too that can affect the wattage of your PSU, but these are the most important ones.
Now that we know which hardware requires more power concentration, we can move to our hardware requirements.
How Do I Know What Power Supply I Need?

A sufficient amount of wattage is required for your PC build to cover the power requirements of all components. To determine this, multiply the total amps of all components by the total volts of all components, yielding the total number of watts required by an equivalent PSU capable of completing your PC build.
The result helps you get a power supply that is compatible with your current or future PC build. Before you come across the recommended power supplies, I’ll make sure you consider all of the important aspects of your search. You will need to cover the needs of the following computer components to reach the appropriate power supply:
PC Components That Need Power To Run
- Motherboard,
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Graphics Processing Units (GPUs),
- Random Access Memory (RAM),
- PC Case Cooling Fans,
- RGB Lightning (Fan And RGB Controllers),
- Central Processing Unit Cooler (CPU Cooler Or Liquid Cooling),
- Graphics Processing Unit Coolers (GPU Waterblock),
- Solid State Drives (SSDs),
- Hard Disk Drives (HDDs),
These are the main components that require power from your computer’s power supply unit (PSU). Knowing how much power your system component requires will simplify your purchase of a power supply unit.
The above factors in watts strongly recommend the PSU wattage to efficiently power your PC with enough power to run it very smoothly for the desired purpose of gaming, workstation, or office build.
Selection Of Ideal Power Supply For Gaming PC
- Components, such as VGA cards, PCI devices, external HDDs and storage devices, cooling fans, RGBs, and others, may consume additional power, which is why going for an increased wattage PSU is recommended.
- You must calculate all component requirements for Amps and Volts to get the equivalent power supply. When considering a gaming build, it is preferable to get a slightly more powerful gaming PSU that is at least 550W and cable to meet all-powerful component requirements, including future upgrades.
How Many Types Of Computer Power Supplies Are There?
Computer power supplies come in a variety of shapes and sizes. Still, all performance factors are a little different but with the same basic function: to convert AC power from the wall into DC power that your computer can use. But what if you could choose between a smaller, more compact power supply that runs a little bit hotter or a larger one that’s quieter and cooler?
That’s because there are three different types of computer power supplies, each with its advantages and disadvantages. These three types of computer power supplies are available for regular office computers, workstations, and gaming PCs: ATX, ATX12V, and SFF or ITX.
What Are The 3 Types Of Computer Power Supply?

The form factor of a power supply helps you choose the right power supply you need for a PC. Down below are the types that you can ensure your power supply will fit in your PC case with the right size and cable connectors.
The three types of computer power supplies are ATX, ATX12V, and SFF:
ATX PSU
The ATX power supply is the most common type of power supply and is typically used in midsize desktop computers. It has a 20 or 24-pin main connector and a 4-pin auxiliary connector.
ATX12V PSU
The ATX12V is used in some full-size desktop computers and most mid-size PCs. It has a 24-pin main connector and a 4-pin auxiliary connector.
ITX Or SFF PSU
The compact form factor SFF (ITX powers supply) is used in small form factor desktop computers and some ATX cases. It has a 6-pin main connector.
How Do I Know What Power Supply I Need From Three Types?
The most common type of computer power supply is the ATX form factor. ATX power supplies are about 5.9″ by 3.4″ by 2.5″, (150mm width, 86mm height, 140mm depth) and they are powerful with an output of around 200W to 2000 watts of power. They’re also very efficient, which means they don’t generate a lot of heat, and they’re relatively quiet.
If you are building a mid-tower PC, an ATX power supply can be a great option. Despite this, you have an option to go for a larger ATX12V type which can benefit your full tower build. Otherwise going for SSF is recommended for small form-factor (SFF power supplies).
Cable Connector Classification: Modular Vs Non-Modular Vs Semi-Modular Power Supplies
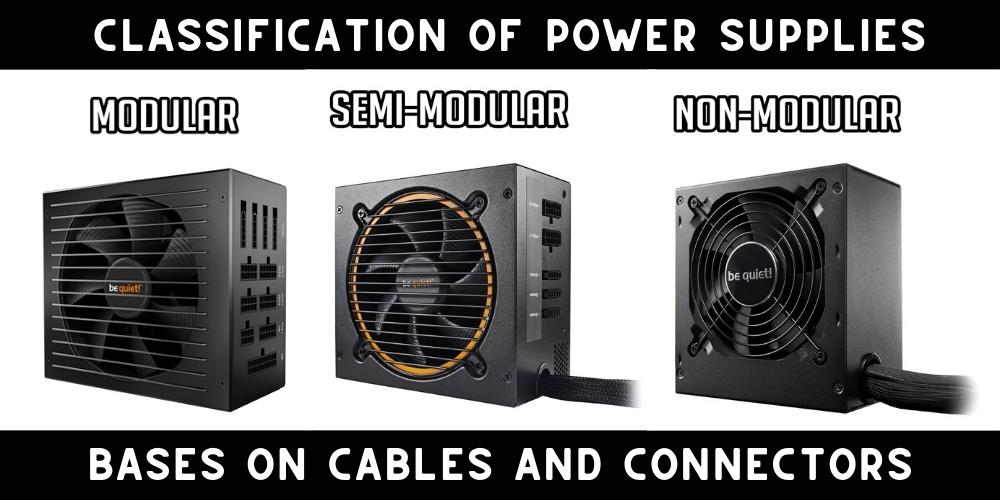
The difference between the modular, non-modular, and semi-modular power supplies is the classification of their cables and connectors, which differs them from each other for usability no in terms of wattage differences. To know the classification for modern PSUs that differ from cables and connectors, here are the differences.
Modular Power Supply
The most advanced modular power supplies are a popular choice in the tech industry because they offer a number of advantages over other types of power supplies like non-modular power supplies. The MPSU has the option of having all of its cables and connectors detachable.
This means that users can connect cables as needed and spares others for upgrades, as opposed to the non-modular, last-generation standard type, which offers permanently fused cables to the unit.
The image above depicts the distinction between a modular and non-modular power supply. But they also have a disadvantage that semi-modular power supplies mitigate.
Non-Modular Power Supply
The non-modular power supplies are those that are not broken down into individual components like a modular supply. They come as one large unit and must be installed as a whole. The type has already infused cables for the whole system build, which certainly has an advantage and a drawback.
The advantage of a non-modular PSU is that you don’t need extra cables for motherboard connections; simply use the pre-installed cable and plug in your PC components. However, if you do not want to add every additional device, this is a drawback, you have to eliminate the extra cables that must be hidden, and cable management is another issue. Because of this, non-modular power supplies can be more difficult to work with than modular supplies.
Semi-Modular Power Supply
The semi-modular power supplies are those that come with some cables, but not all, of their components pre-separated, which means they have all the necessary and supported cables with connectors, such as the main cable with a 24-pin connector, an 8-pin CPU cable, and a PCIe cable.
This reduces the hassle and suitable types for new builds as well as small systems. This makes them easier to install than a modular supply and takes up slightly less space.
How Big Of A Power Supply Do I Need For My Gaming PC?

Many modern gaming systems with a 6 or 8-core CPU and a mid-range to the high-end graphics card that is rated for medium power consumption. You should be fine with a range from 500W to 850W power supply. Well, 660W and most common 750W has long been gamers’ favorite for a decent build, who are content with a mid-range GPU.
Unlike those gaming PCs that have big and powerful components such as a top-of-the-line GPU like the RTX 3090, a waterblock for liquid cooling, and a high-caliber processor with more than 12 cores, you will need to consider a 1000W PSU, which is recommended to go for a reliable unit such as this, Seasonic Prime Titanium TX-1000m which I’ve found to be the reliable 1K PSU.
The high wattage requirement is because more powerful hardware, particularly if you intend to overclock it for increased bit performance, needs an equivalent or higher power supply.
CPU And GPU Power Consumption Chart For Choosing The Best PSU
| Options | OEM | PSU Wattage | Suitable CPU | Suitable GPU |
| 1 | AMD | 550W PSU | Ryzen 5 3600 | Radeon RX 6600 XT |
| 2 | INTEL | (Corsair RM550X) | Intel Core i5-11400 | Nvidia RTX 2060 Super |
| 3 | AMD | 650W PSU | Ryzen 7 5600X | Radeon RX 6700 XT |
| 4 | INTEL | (XPG Core Reactor 650W) | Intel Core i5-11600K | Nvidia RTX 3060Ti |
| 5 | AMD | 750W PSU | Ryzen 7 5800X | Radeon RX 6700 XT |
| 6 | INTEL | (Corsair RM750X) | Intel Core i7-9700K | Nvidia RTX 3070Ti |
| 7 | AMD | 850W PSU | Ryzen 9 5900X | Radeon RX 6800 XT |
| 8 | INTEL | (Corsair RM850X) | Intel Core i7-11700K | Nvidia RTX 3080Ti |
| 9 | AMD | 1000W PSU | Ryzen 9 5950X | Radeon RX 6900 XT |
| 10 | INTEL | (Seasonic Prime Titanium TX-1000) | Intel Core i9-11900K | Nvidia RTX 3090 |
Can You Start A PC Without A PSU?
In an age where most devices need to be plugged into the wall outlet to function, it’s hard to imagine a device that doesn’t require a power source. But believe it or not, some devices can be started without a power supply. PCs are not one of them.
At least, that’s a common belief. In reality, you can start a PC without a PSU, but it won’t be able to do much. All the components in your PC need the right amount of power to function, and if you don’t have a PSU with compatible cables with the right type of 24-pin and 12-pin connectors for individual hardware like GPU, PC fans, and storage drives, you won’t be able to provide that power with a direct wall outlet.
In other scenarios, what can you do if your PSU dies and you don’t have a spare? There are a few things you can try:
- If you have an old power supply lying around with lower wattage, you can use it to start your PC for basic work.
- You can use an alternate low power supply with less hardware bundle, such as removing your dedicated GPU to rely on iGPU and no more storage disc other than the boot drive.
- However, this is no permanent solution, unless you have the capable power supply unit for your appropriate hardware.